
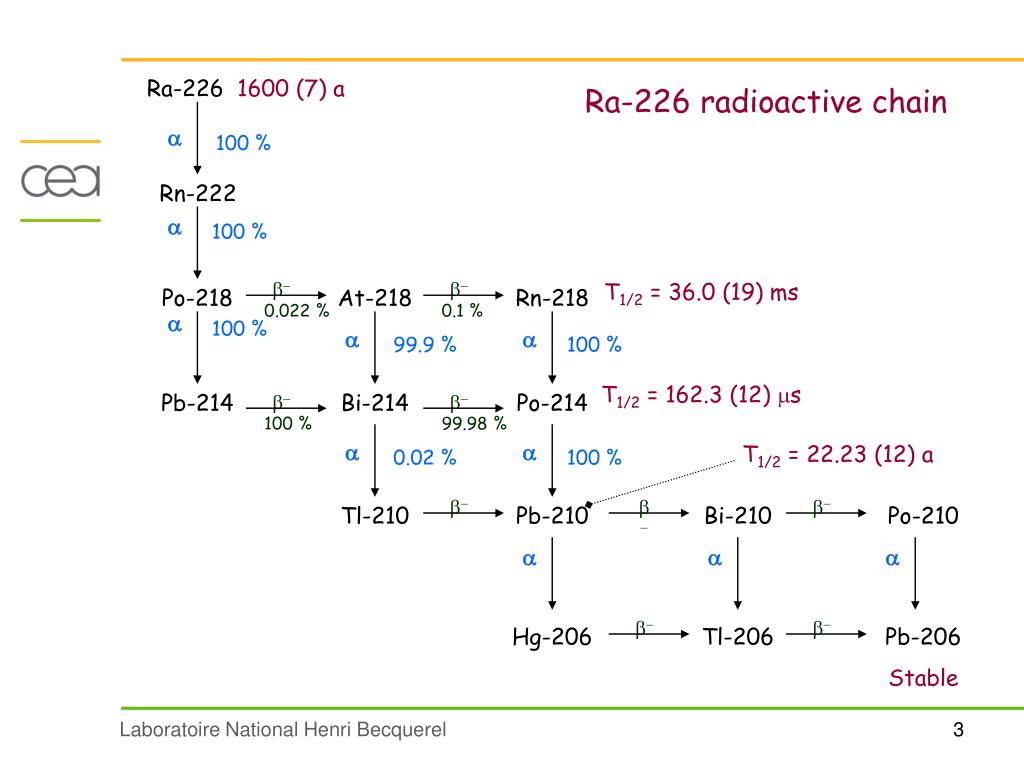
The next radioisotope in the uranium series is radon, radon-222. Data extracted from NUDAT database (Dec.18, 1997). of its similarity to calcium, radium-226 is stored mainly in the bone, and it produces abnormal changes in the bone marrow, including anemia and leukemia, cancers of the bone, and paranasal sinuses. R.R.Kinsey, et al., The NUDAT/PCNUDAT Program for Nuclear Data, paper submitted to the 9 th International Symposium of Capture-Gamma_ray Spectroscopy and Related Topics, Budapest, Hungary, Octover 1996. The entries are taken from the NUDAT database, see: Pb-206 is the final product of the U-238 radioactive series. Levels of radium-226 in the rainbow trout, macroinvertebrates-substrates and water adjacent to the mining concession Loma Larga, Azuay-Ecuador. (Historically Pb-206 is also called Radium G) (Historically Po-210 is also called radium F) All isotopes of radium are radioactive, the most stable isotope being radium-226 with a half-life of 1,600 years. for 10 nuclides, from Ra-226 ending at Pb-210 as shown in gure 1. It is also a strong alpha emitter, as are most of its short-lived progeny, hence it can generate relatively heavy radiological doses in. 226 Ra is a divalent cation taken up as a biological analogue of the major nutrient, Ca. Decay chain of Ra-226 evaluated in this work. Radium-226 and 210 Po are the most commonly evaluated U-series nuclides on the basis of their potential radiotoxicities. In this work, the evaluation of gamma and alpha emissions were performed Fig. (Historically Bi-210 is also called radium E) The natural radioactive Ra-226 decay chain includes 13 nuclides, ending at the stable isotope of Pb-206. desorption from the soil and washoff by rain water) or can be released from technological processes involving naturally occurring. (Historically Pb-210 is also called radium D) Natural radionuclides, including 40 K, 3 H, 14 C, and those originating from the thorium and uranium decay series, in particular 226 Ra, 228 Ra, 234 U, 238 U and 210 Pb, can be found in water for natural reasons (e.g. (Historically Tl-210 is also called radium C")

(Historically Po-214 is also called radium C') Subsequently γ radiation of Po-214 at 609 keV possible It is based upon recording the alpha radiation of Rn-222 and its decay products Po. (Historically Bi-214 is also called radium C) The principle of the procedure is described in procedure H-Ra-226-TWASS-01. Subsequently γ radiation of Bi-214 at 352 keV, 295 keV, 242 keV, 53 keV possible 83-Bi-214 (Historically Pb-214 is also called radium B) (Historically Po-218 is also called radium A) The radium target was prepared by electroplating. Subsequent ion-exchange purification gave pure 226 Ra with a certain amount of carrier Ba. 226 Ra was extracted from legacy Ra sources using a chelating resin. Subsequently γ radiation of Rn-222 at 186 keV possible 86-Rn-222 We demonstrate cyclotron production of high-quality 225 Ac using an electroplated 226 Ra target. Open topic with navigation The radioactive series of radium-226


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
